AI Chat Dashboard User Guide
Learn how to turn the Onyx Cloud AI Chat workspace into a productive AI assistant for data analysis, schema exploration, and operational automation. This guide covers chat streams, query generation, execution guard rails, and research integrations so you can collaborate with confidence.
Introduction
AI Chat brings the Onyx AI expert directly into the admin console. Each conversation is aware of your active organization, database schema, and saved queries, enabling the assistant to draft scripts, execute them (with approvals), summarize schema insights, and pull in external research—all from a single thread.
Purpose-built AI assistant
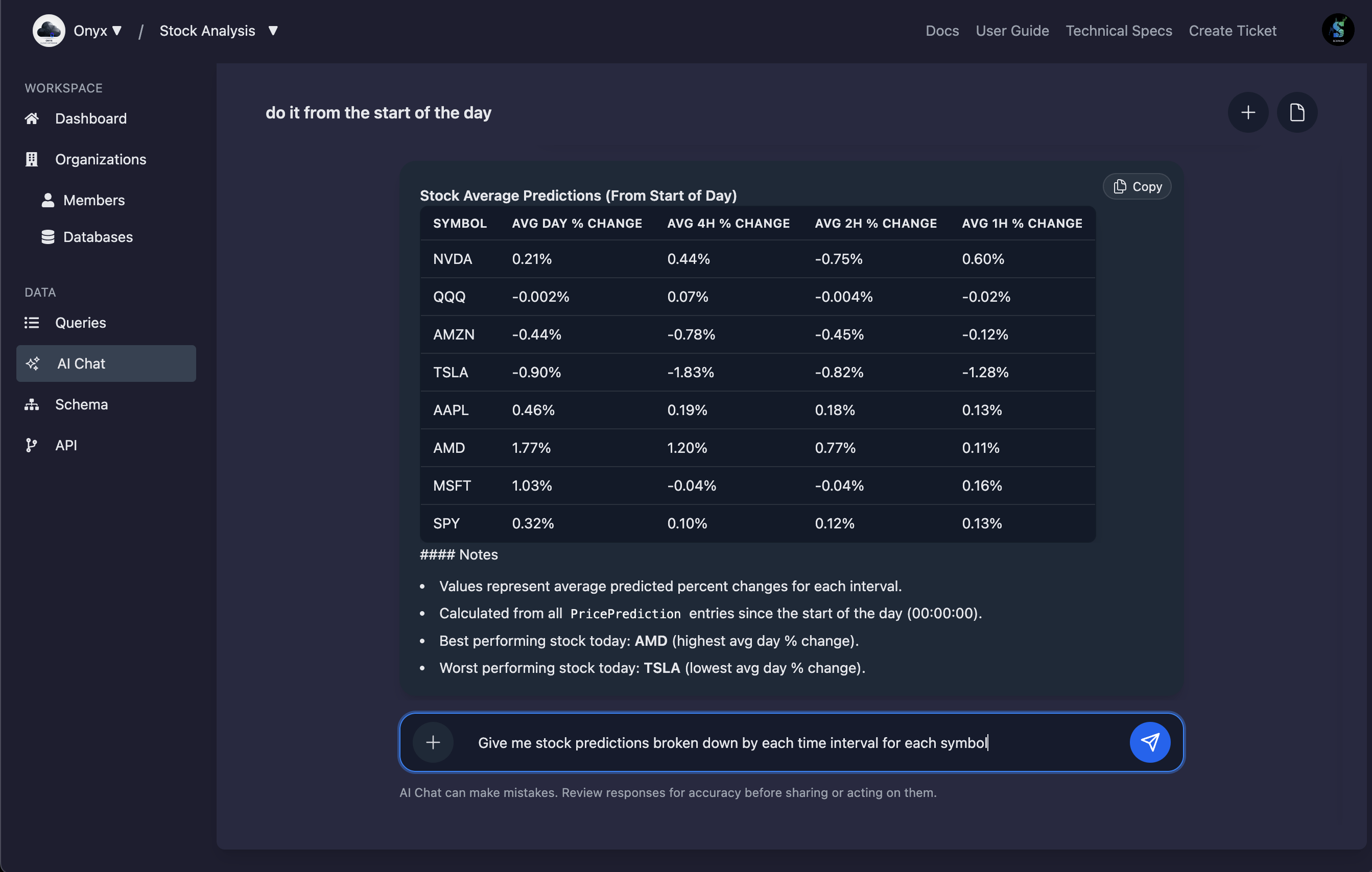
The assistant uses multi-step planning to analyze schema metadata, collaborate with the Query Assistant, and return formatted results you can run in the console.
Governed execution
Before mutations run, the chat requests your approval, documenting the script and highlighting the risky operations detected by automated guards.
Access Requirements & Context
AI Chat inherits the current organization, database, and schema context from the admin console. Ensure you meet the following prerequisites before starting a conversation:
- Authenticated user: You must be signed in so the assistant can retrieve Firebase tokens and authorize API calls on your behalf.
- Selected organization: Pick an organization in the top-level context switcher. The chat API stores threads per organization, so the assistant can load historical conversations.
- Active database: Choose a database to expose its schema to the AI and to enable query execution against the correct environment.
- Current schema metadata: Visit the schema or query editor at least once so the generated introspection is cached for the assistant’s planning prompts.
Navigating the Workspace
The AI Chat workspace is designed around persistent chat streams. Each stream maintains its own title, preview, and message history so you can organize work by task, feature, or stakeholder.
- Streams panel: Use the right-side panel to search, rename, or delete chats. Streams display recency, previews, and tooltips to help you triage ongoing conversations.
- Message timeline: Assistant messages can surface MCP tool output, query history cards, and inline markdown for quick reading.
- Composer: Draft prompts, attach saved queries, or send Shift+Enter multi-line messages without leaving the console.
Starting and Managing Chats
Follow these steps to spin up a new conversation or resume an existing one:
Open AI Chat from the sidebar
Click AI Chat in the left navigation. The app loads persisted chat streams for your organization and selects the most recent conversation.
Start a new stream
Use the New Chat button in the header to create a fresh stream. The assistant auto-generates a title and preview based on the first message you send.
Search and curate history
Filter the streams list by keyword to locate prior research. Delete drafts or archived chats to keep the workspace focused on current initiatives.
Attaching Saved Queries
Provide the assistant with precise technical context by attaching queries from the saved library:
- Attachment menu: Click the plus icon beside the composer to open a searchable list of saved queries scoped to the active database.
- Inline previews: Selected queries appear as chips above the composer and expand inside the sent message so you can review code alongside the chat response.
- Automatic markup: When the message is sent, AI Chat inlines a Markdown code block for each attachment, making it easy for the assistant to reference and modify existing scripts.
Schema-Aware Planning & Prompts
Every chat turn begins with a system prompt that embeds your schema, SDK contract, and MCP (Model Context Protocol) usage instructions. This ensures the assistant plans with Onyx-specific knowledge without extra setup from you.
- Dynamic schema summaries: The assistant prioritizes the generated schema from the database introspection API, falling back to saved API schemas when necessary.
- SDK-first guidance: Prompt instructions reinforce the Onyx Database SDK helpers (e.g.,
db.from(),eq(),and()) and discourage raw SQL so generated scripts remain portable. - MCP orchestration: The built-in instruction block describes how to call tools such as generate-script, execute-query, web-search, and read-web-page without exposing intermediate markup to end users.
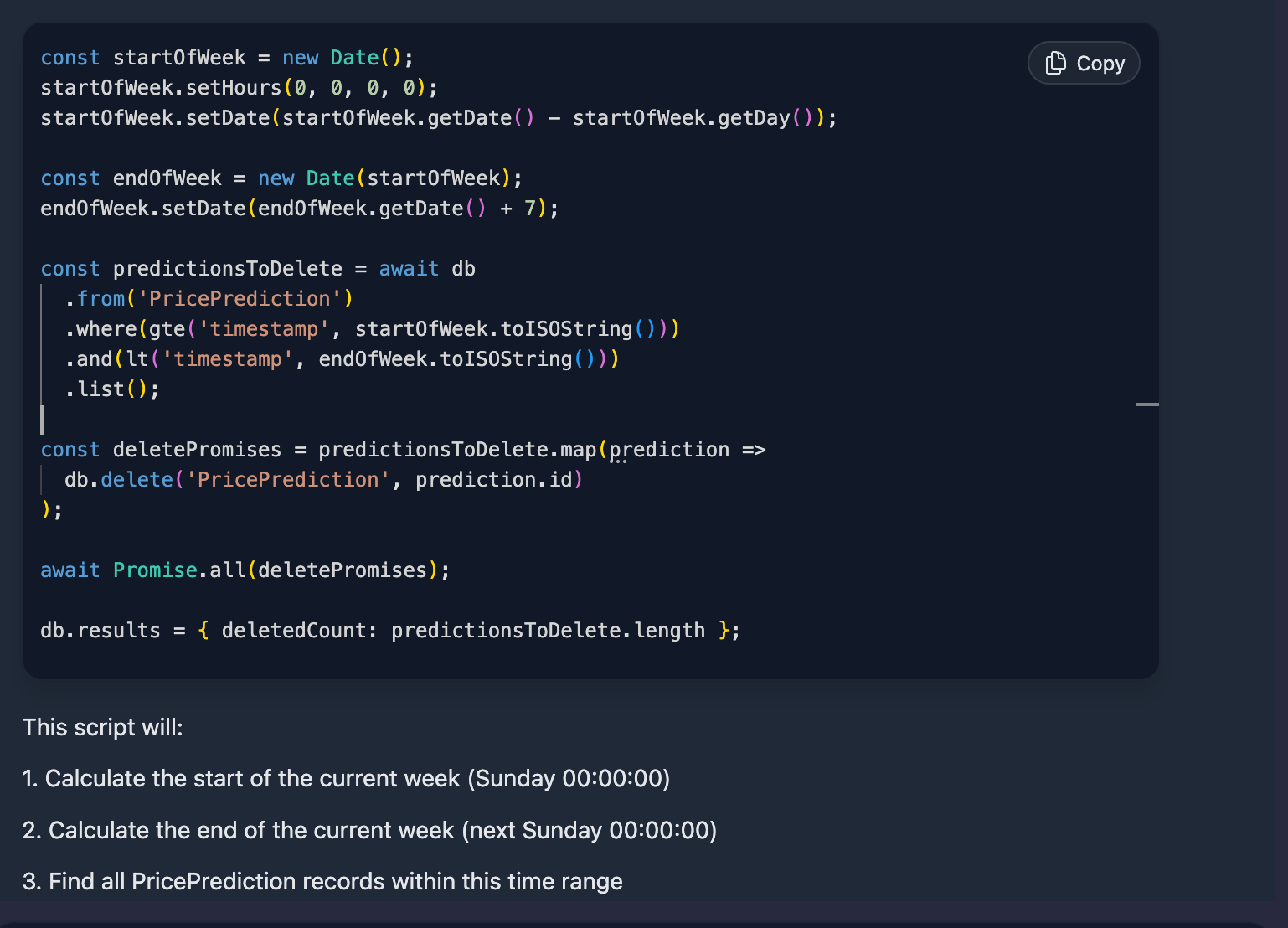
Generating Query Scripts
When the assistant needs code, it collaborates with the Query Assistant via the generate-script MCP function. The workflow looks like this:
- Draft the intent: Your prompt (and any attached queries) are summarized into a goal that guides the script request.
- Schema-aware request: The assistant supplies the latest schema summary and optional existing script to the Query Assistant endpoint, which streams a TypeScript response.
- Quality checks: If the response lacks a valid code block, AI Chat reports the error and asks for clarification, maintaining transparency.
Executing Queries with Guard Rails
Execution happens through the execute-query MCP function, which runs code in a secure web worker using your authenticated Onyx Database session. Guard rails keep production data safe:
- Mutation detection: Scripts are scanned for patterns such as
.save(),.insert(),.delete(), and.transaction(). If a match is found, you must explicitly approve the run from the modal dialog. - Short-lived approvals: Once granted, approvals expire quickly and are tied to the exact normalized script to prevent replay attacks.
- Rich telemetry: Each execution returns status codes, log output, JSON/typed results, and script previews, so you can debug failures or share reproducible snippets with teammates.

Web Research & Content Extraction
Combine database insights with market or documentation research without leaving the chat:
- web-search: Performs DuckDuckGo lookups (capped at eight results) using a privacy-friendly HTML endpoint. Useful for competitive research, industry benchmarks, or API references.
- read-web-page: Fetches and cleans page text, exposing metadata, truncated HTML, and HTTP status info so you can cite authoritative sources in responses.
- Responsible usage: The assistant only invokes these tools when needed, summarizing the output in plain language and linking to the original URLs in follow-up messages.
Auditing Results & History
Governance requires visibility. AI Chat embeds a structured history for every tool call:
- Hidden MCP transcripts: Each tool invocation is stored in the thread so the assistant can reason over past attempts without overwhelming the UI.
- Query history cards: Visible messages render execution summaries—status, duration, preview, and JSON—making it easy to reproduce or roll back changes.
- Copy-friendly responses: Use the inline copy buttons to share assistant output or scripts in pull requests, incident runbooks, or stakeholder updates.
Troubleshooting & Best Practices
- Refresh schema often: If results seem stale, revisit the schema explorer so AI Chat can rehydrate its metadata context.
- Break down complex tasks: Large goals work best when decomposed into smaller prompts. Let the assistant complete one outcome before moving to the next.
- Review approvals carefully: Mutation guards are intentionally strict. Read the highlighted matches before approving to ensure scripts do exactly what you expect.
- Capture learnings: Rename streams with meaningful titles and keep critical chats pinned so your team can revisit successful investigations.
Next Steps
Need Help?
If you have any questions or need assistance:
- Email:support@onyx.dev
- Documentation: Visit ourHelp Centerfor tutorials and FAQs.